Gabor Layers Enhance Network Robustness
这篇paper提出将gabor filter 用于替代卷积层.能得到更鲁邦更丰富的features.

Gabor Filter
Gabor Filter 是一个仿生地线性滤波器,可以理解为一个被高斯调制过的正弦函数. 有一个比较好的medium教程
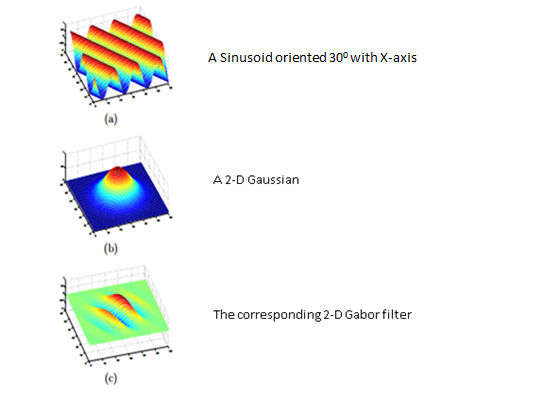
- :高斯方差
- :spatial aspect ratio
- :平行条纹的法向
- :相位
- : 正弦波长
Gabor Layer

上文中的提到的五个参数除了皆为系统可直接学习参数。在间均匀采样的角度.
实现上,由depth-wise gabor filter convolution 与 普通 conv组成
Regularization
作者把前向函数Lipschitz连续性与robustness联系起来,而gabor filter的lipschitz常数为:
在损失函数上的修改为:
代码实现
import torch
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GaborLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding,
kernels, extra_kernels=0, orientations=8, bias1=False,
bias2=False, relu=True, use_alphas=True):
super(GaborLayer, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.stride = stride
self.padding = padding
self.kernels = kernels
self.orientations = orientations
self.extra_kernels = extra_kernels
self.total_kernels = self.kernels + self.extra_kernels
self.responses = self.kernels * self.orientations + self.extra_kernels
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.relu = relu
self.use_alphas = use_alphas
# Replicate parameters so that broadcasting is possible
self.Lambdas = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.total_kernels).unsqueeze(
dim=1).unsqueeze(dim=2).unsqueeze(dim=3))
self.psis = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.total_kernels).unsqueeze(
dim=1).unsqueeze(dim=2).unsqueeze(dim=3))
self.sigmas = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.total_kernels).unsqueeze(
dim=1).unsqueeze(dim=2).unsqueeze(dim=3))
self.gammas_y = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.total_kernels).unsqueeze(
dim=1).unsqueeze(dim=2).unsqueeze(dim=3))
if self.use_alphas:
self.alphas = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.responses).unsqueeze(
dim=1).unsqueeze(dim=2))
# Bias parameters start in zeros
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(self.responses)) if bias1 else None
# # # # # # # # # # # # # # The meshgrids
# The orientations (NOT learnt!)
thetas = torch.arange(0., self.orientations) * 2 * np.pi / self.orientations
self.thetas = nn.Parameter(thetas, requires_grad=False)
# The original meshgrid
# Bounding box
xmin, xmax = -1, 1
ymin, ymax = -1, 1
x_space = torch.linspace(xmin, xmax, kernel_size)
y_space = torch.linspace(ymin, ymax, kernel_size)
(y, x) = torch.meshgrid(y_space, x_space)
# Unsqueeze for all orientations
x, y = x.unsqueeze(dim=0), y.unsqueeze(dim=0)
# Cosines and sines
cosines = torch.cos(self.thetas).unsqueeze(dim=1).unsqueeze(dim=1)
sines = torch.sin(self.thetas).unsqueeze(dim=1).unsqueeze(dim=1)
self.x = x * cosines - y * sines
self.y = x * sines + y * cosines
# Expand for the number of kernels
self.x, self.y = self.x.unsqueeze(dim=0), self.y.unsqueeze(dim=0)
# Add as parameters
self.x = nn.Parameter(self.x, requires_grad=False)
self.y = nn.Parameter(self.y, requires_grad=False)
# Some precomputed values
self.x_sq = nn.Parameter(self.x**2, requires_grad=False)
self.y_sq = nn.Parameter(self.y**2, requires_grad=False)
# Conv1x1 channels
self.channels1x1 = self.responses * self.in_channels
self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=self.channels1x1, out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=1, bias=bias2)
def forward(self, x):
# Generate the Gabor kernels
if not hasattr(self, 'gabor_kernels'):
self.gabor_kernels = self.generate_gabor_kernels()
if self.training:
self.gabor_kernels = self.generate_gabor_kernels()
# kernels are of shape
# [self.kernels*self.orientations + self.extra_kernels, 1, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size]
# Reshape the input: x is of size
# [batch_size, in_channels, H, W]
# and we need to merge the batch size and the input channels for the
# depthwise convolution (and include a '1' channel for the convolution)
bs, _, H, W = x.size()
x = x.view(bs*self.in_channels, H, W).unsqueeze(dim=1)
# Perform convolution
out = F.conv2d(input=x, weight=self.gabor_kernels, bias=self.bias,
stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding)
if self.relu:
out = torch.relu(out)
# 'out' is of size [batch_size*in_channels, newH, newW]
_, _, newH, newW = out.size()
# reshape to:
out = out.view(bs, self.in_channels, self.responses, newH, newW)
# now reshape to
out = out.view(bs, self.channels1x1, newH, newW)
return self.conv1x1(out)
'''
Inspired by
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gabor_filter
'''
def generate_gabor_kernels(self):
# Precompute some squared terms
gammas_y_sq = self.gammas_y**2
sigmas_sq = self.sigmas**2
# ORIENTED KERNELS
# Compute Gaussian term
# gaussian_term = torch.exp(-.5 * ( (gamma_x**2 * x_t**2 + gamma_y**2 * y_t**2)/ sigma**2 ))
ori_y_term = gammas_y_sq[:self.kernels] * self.y_sq
exponent_ori = (self.x_sq + ori_y_term) * sigmas_sq[:self.kernels]
gaussian_term_ori = torch.exp(-exponent_ori)
# Compute Cosine term
# cosine_term = torch.cos(2 * np.pi * x_t / Lambda + psi)
cosine_term_ori = torch.cos(self.x * self.Lambdas[:self.kernels] + self.psis[:self.kernels])
# 'ori_gb' has shape [self.kernels, self.orientations, kernel_size, kernel_size]
ori_gb = gaussian_term_ori * cosine_term_ori
# Combine the first two dimensions
ori_gb = ori_gb.view(self.kernels * self.orientations, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size)
if self.extra_kernels > 0:
# NON-ORIENTED KERNELS (take the first channel of x and y)
# Compute Gaussian term
# gaussian_term = torch.exp(-.5 * ( (gamma_x**2 * x_t**2 + gamma_y**2 * y_t**2)/ sigma**2 ))
y_term = gammas_y_sq[self.kernels:] * self.y_sq[:, :1]
exponent = (self.x_sq[:, :1] + y_term) * sigmas_sq[self.kernels:]
gaussian_term = torch.exp(-exponent)
# Compute Cosine term
# cosine_term = torch.cos(2 * np.pi * x_t / Lambda + psi)
cosine_term = torch.cos(self.x[:, :1] * self.Lambdas[self.kernels:] + self.psis[self.kernels:])
# 'gb' has shape [self.extra_kernels, 1, kernel_size, kernel_size]
gb = gaussian_term * cosine_term
# Collapse singleton dimension
gb = gb.squeeze(dim=1)
# Join oriented and non-oriented filters
ori_gb = torch.cat([ori_gb, gb], dim=0)
if self.use_alphas:
ori_gb = self.alphas * ori_gb
return ori_gb.unsqueeze(dim=1)